A Comprehensive Guide on How to Decipher a QR Code
To create a QR code for a link, video or picture - click on the button below.

QR codes have become an integral part of our daily lives, appearing on everything from product packaging to business cards and event tickets. Understanding QR codes is essential for anyone looking to leverage this technology for personal or professional use.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the structure of QR codes, various types, tools, and techniques for deciphering them, practical applications, and best practices for creating effective QR codes. By the end of this article, you will have a thorough understanding of how to decode QR codes and apply this knowledge in various contexts.
Understanding the Structure of a QR Code
To effectively decode a QR code, it's crucial to understand its structure. A QR code (Quick Response code) is a two-dimensional barcode that can store a significant amount of data. The structure of a QR code comprises several key components, each serving a specific function to ensure accurate decoding. By breaking down these components, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the intricacies involved in QR code design and functionality.
Components of a QR Code
QR codes consist of various elements that work together to store and convey information. Here, we break down the main components, highlighting their roles and importance in the overall structure of the QR code.
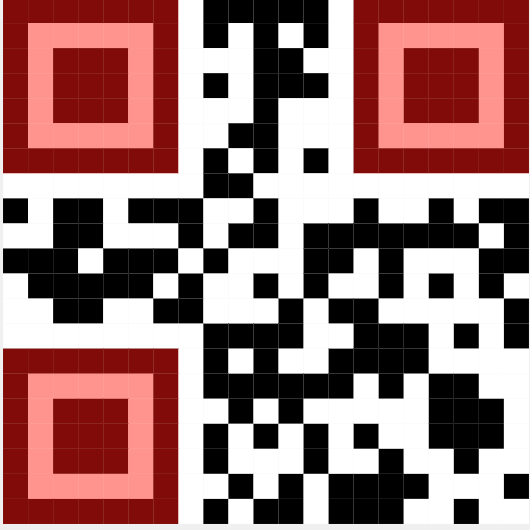

Finder Pattern
The finder pattern is one of the most recognizable features of a QR code, consisting of three large squares located at the corners of the QR code. These squares are crucial for the QR code reader to detect the code's position and orientation.
By identifying the finder patterns, the reader can quickly determine the alignment, which is essential for accurate QR code decoding and scanning. The consistent placement of these patterns ensures that QR codes can be scanned from multiple angles and under various lighting conditions.
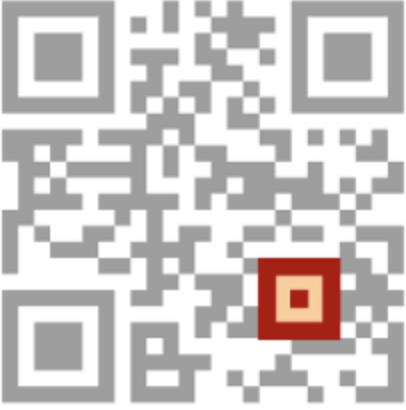

Alignment Pattern
The alignment pattern is a smaller square that appears in larger QR codes. Its primary function is to ensure the QR code can be read accurately, even if it is distorted due to scanning at an angle or on a curved surface.
The alignment pattern helps the reader align the code correctly, compensating for any potential distortions and ensuring that the data cells can be accurately interpreted. This feature is particularly important for larger QR codes, where the increased size can make them more susceptible to scanning errors.

Timing Pattern
The timing pattern consists of a series of alternating black and white modules that run horizontally and vertically between the finder patterns. This pattern helps the reader determine the size of the data matrix and locate the data cells within the QR code.
By establishing a consistent timing pattern, the reader can accurately interpret the positioning of the data cells, regardless of any potential distortions or alignment issues. The timing pattern acts as a reference grid, ensuring that the data cells are read correctly and consistently.
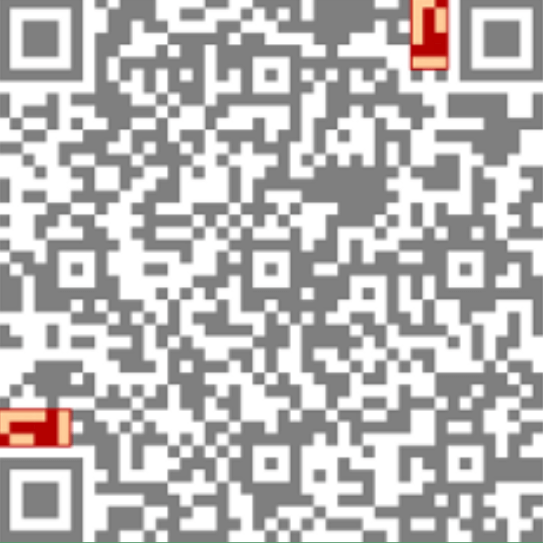

Version Information
QR codes come in different versions, ranging from version 1 to version 40. The version information is encoded within the QR code itself, indicating the QR code's size and data capacity. As the version number increases, so does the number of modules and the amount of data that can be stored.
The version information allows the reader to understand the specific layout and capacity, ensuring that it is possible to decrypt QR code accurately regardless of its complexity. This scalability is one of the key features that make QR codes versatile and adaptable to various applications.
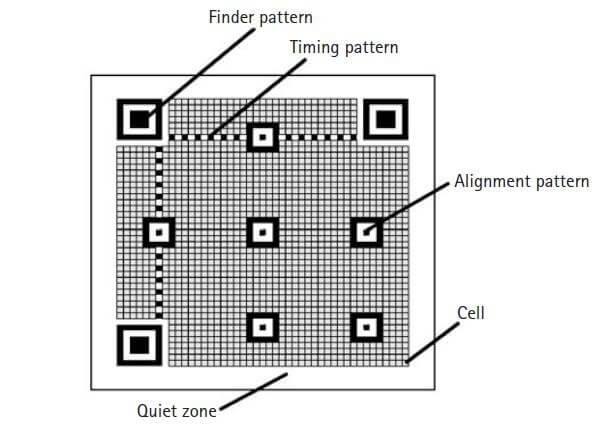

Data Cells
Data cells are the smaller black and white squares that store the encoded information within the QR code. These cells represent binary data, which can be decoded to reveal the stored content.
The arrangement of data cells follows a specific encoding format, ensuring that the information can be accurately interpreted by the reader. The density and arrangement of these cells determine the amount of data that can be stored in the QR code, making it essential to design the data cells carefully to maximize both capacity and readability.
Different Types of QR Codes
QR codes come in various types, each designed for specific uses and functionalities. Understanding these types helps in choosing the right QR code for a particular application. The two main categories of QR codes are static and dynamic, each offering unique features and benefits.

Static QR Codes
Static QR codes contain fixed information that cannot be changed once generated. These codes are ideal for storing information that doesn't need to be updated, such as URLs, contact details, or product information. Static QR codes are simple to create and do not require any ongoing maintenance or updates. They are commonly used in applications where the encoded information remains constant, providing a reliable and straightforward solution for data storage.
Common use cases for static QR codes include:
-
Business Cards: Storing contact details such as name, phone number, and email address.
-
Product Packaging: Providing links to product information, user manuals, or warranty details.
-
Signage: Offering quick access to websites or informational resources.
-
Coupons and Vouchers: Delivering fixed discount codes or promotional offers.
Despite their simplicity, static QR codes have some limitations. Since the information is fixed, any changes to the encoded data require the creation of a new QR code. Additionally, static QR codes cannot track usage or gather analytics, limiting their effectiveness in dynamic marketing campaigns.
Dynamic QR Codes
Dynamic QR codes, on the other hand, allow for the encoded information to be edited even after the code has been printed. This flexibility makes them suitable for applications like marketing campaigns, where the destination URL or information might need to be updated frequently. Dynamic QR codes store a short URL that redirects to the actual content, allowing the encoded information to be changed without altering the QR code itself. This feature provides significant advantages in terms of flexibility and functionality.
Key benefits of dynamic QR codes include:
-
Updatability: Easily update the encoded information without changing the QR code.
-
Analytics: Track scans and gather data on user interactions.
-
Personalization: Customize content based on user preferences or behaviors.
-
Security: Implement access controls and authentication for sensitive information.


Dynamic QR codes are ideal for applications that require frequent updates or where tracking and analytics are important. Common use cases include:
-
Marketing Campaigns: Redirecting to different promotional content based on the campaign phase.
-
Event Management: Updating event details, schedules, or ticket information.
-
Inventory Management: Changing product information or availability status.
-
Payments: Facilitating secure transactions and updating payment details.
While dynamic QR codes offer greater flexibility and functionality, they often require a subscription or service to manage and update the encoded information. Additionally, the reliance on a redirection URL introduces a potential point of failure if the redirection service is unavailable.
Tools and Techniques to Decrypt a QR Code
Decoding a QR code can be done using various methods and tools, including smartphones, computers, and manual techniques. Each method has its advantages and specific use cases. Understanding the available tools and techniques ensures that you can efficiently decode QR codes in any situation.
Using a Smartphone
Smartphones are the most common tools when it comes to “how to decode a QR code?” due to their convenience and widespread availability. With built-in cameras and dedicated apps, smartphones offer a quick and easy way to access the information stored in a QR code.

Built-in Camera Apps
Most modern smartphones come with built-in camera apps that can scan QR codes directly. The process is straightforward: simply open the camera app, point it at the QR code, and a notification will appear with the decoded information. This feature is integrated into the camera software of many smartphones, making it a hassle-free solution for scanning QR codes.
Benefits of using built-in camera apps include:
-
Convenience: No need to download additional apps.
-
Speed: Instant recognition and decoding of QR codes.
-
Accessibility: Available on most modern smartphones.
However, built-in camera apps may have limitations in terms of advanced features or compatibility with certain QR code types. For users requiring more functionality, third-party QR code reader apps provide a robust alternative.

Third-Party QR Code Reader Apps
There are numerous third-party apps available for QR code scanning, offering additional features and functionalities. These apps often provide enhanced scanning capabilities, support for various QR code types, and additional tools for managing decoded information. One popular app is the ME-QR Scanner, which provides a user-friendly interface and a range of features for efficient QR code scanning.
Features of the ME-QR Scanner include:
-
Support for Multiple QR Code Types: Scan and decode various types of QR codes, including static and dynamic codes.
-
Enhanced Scanning Capabilities: Improved accuracy and speed in scanning QR codes under different conditions.
-
Data Management: Save and organize scanned QR codes for future reference.
Using third-party apps can enhance the QR code scanning experience, providing more flexibility and functionality than built-in camera apps. These apps are particularly useful for power users or those who frequently work with QR codes.
Using a Computer
Decoding QR codes using a computer is the second answer to how to decrypt a QR code. It involves online tools and software programs designed for this purpose. Computers offer a more versatile platform for decoding QR codes, allowing users to leverage larger screens and more powerful processing capabilities.

Online QR Code Decoding Tools
Several websites offer online QR code decoding services. Users can upload an image of the QR code, and the website will decode the information and display it. These tools are useful for quick and easy decoding without the need for additional software installation.
Advantages of online QR code decoding tools include:
-
Accessibility: Available from any device with internet access.
-
Ease of Use: Simple upload and decode process.
-
No Installation Required: Decode QR codes without installing software.
While online tools are convenient, they may not offer the same level of functionality as dedicated software programs. Additionally, users must have internet access to use these tools, which may not be practical in all situations.

Software for QR Code Decoding
Dedicated software programs can also be used to decode QR code from image and other types. These programs often provide more advanced features, such as batch processing, detailed analysis of the QR code structure, and offline capabilities.
Benefits of using software for QR code decoding include:
-
Advanced Features: Access to tools and functionalities not available in online tools.
-
Offline Use: Decode QR codes without an internet connection.
-
Batch Processing: Decode multiple QR codes simultaneously, improving efficiency.
Using dedicated software provides a more robust and versatile solution for QR code decoding, particularly for users with advanced needs or those working with large volumes of QR codes.
How to Read a QR Code Manually?
For those interested in a deeper understanding, manually decoding a QR code involves analyzing its structure and understanding the encoding format. While this method is more complex and time-consuming, it offers valuable insights into the inner workings of QR codes.
Analyzing the QR Code Structure
The first step in manual decoding is to interpret the QR code's structure. This involves identifying the finder patterns, alignment patterns, timing patterns, and version information. By understanding the layout and arrangement of these components, you can begin to decode the data cells.
Steps for analyzing the QR code structure:
-
Identify Finder Patterns: Locate the three large squares at the corners of the QR code.
-
Locate the Alignment Pattern: Find the smaller square, typically located near the bottom-right corner.
-
Examine the Timing Pattern: Observe the alternating black and white modules running between the finder patterns.
-
Determine Version Information: Decode the version information to understand the QR code's size and capacity.
-
Analyze Data Cells: Identify the smaller black and white squares that store the encoded information.
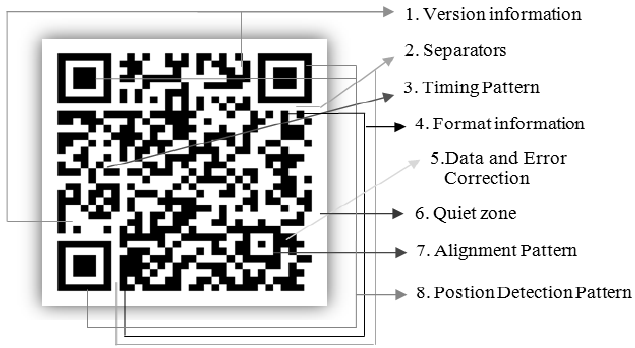
By systematically analyzing these components, you can gain a clearer understanding of the QR code's structure and prepare for the decoding process.

Understanding the Encoding Format
QR codes use different encoding formats, such as numeric, alphanumeric, byte, and Kanji. Each format has specific rules for representing data, which must be understood to accurately decode the information.
Common encoding formats include:
-
Numeric: Encodes numbers using a compact representation, suitable for storing numeric data.
-
Alphanumeric: Encodes both letters and numbers, allowing for a broader range of characters.
-
Byte: Encodes binary data, supporting various character sets and languages.
-
Kanji: Encodes Japanese characters, optimized for storing Kanji and Kana.
If you ask how to read QR codes manually, you must first determine the encoding format used and then interpret the data cells accordingly. This process involves converting the binary data represented by the data cells into readable information based on the encoding rules.
Steps for understanding the encoding format:
-
Identify Encoding Format: Determine the format used by the QR code (numeric, alphanumeric, byte, or Kanji).
-
Interpret Data Cells: Convert the binary data represented by the data cells into characters or values based on the encoding rules.
-
Validate Decoded Information: Verify the decoded content to ensure accuracy and completeness.
Manual decoding requires a thorough understanding of QR code standards and encoding formats, making it a challenging but rewarding process for those interested in the technical aspects of QR codes.
Step-by-Step Guide on How to Decode the QR Code
Decoding a QR code can be broken down into several clear steps, ensuring a systematic approach to deciphering the encoded information. Whether using a smartphone, computer, or manual method, following these steps will help you accurately decode QR codes.
Step One: Choose a Decoding Method
Consider factors such as the availability of devices, the complexity of the QR code, and the need for additional features when selecting a decoding method. Each method has its own advantages and specific use cases.
Factors to consider when choosing a decoding method:
-
Device Availability: Determine if you have access to a smartphone, computer, or need to decode manually.
-
Complexity of QR Code: Assess the QR code's size, type, and any potential distortions or damage.
-
Required Features: Identify if you need additional functionalities such as tracking, analytics, or batch processing.
By evaluating these factors, you can select the most appropriate method and decode the QR code.


Step Two: Scan or Upload the QR Code
Using the chosen method, either scan the QR code with a device or upload an image of the QR code to a decoding tool. This step involves capturing the QR code's image and initiating the decoding process.
Instructions for scanning or uploading the QR code:
-
Using a Smartphone: Open the camera app or a QR code reader app, point it at the QR code, and wait for the notification with the decoded information.
-
Using a Computer: Access an online QR code decoding tool or use dedicated software, upload the QR code image, and follow the prompts to decode it.
-
Manual Method: Capture a clear image of the QR code and analyze its structure as described in the manual decoding process.
Ensuring a clear and accurate capture of the QR code image is crucial for successful decoding.
Step Three: Analyze the Data
Once decoded, analyze the data to interpret the information accurately. This step involves verifying the decoded content and ensuring it matches the intended information.
Steps for analyzing the decoded data:
-
Verify Accuracy: Check the decoded information for accuracy and completeness.
-
Interpret Content: Understand the decoded data and its relevance to your needs.
-
Troubleshoot Issues: If the decoded information is incorrect or incomplete, review the QR code image and decoding process to identify any potential issues.
By carefully analyzing the decoded data, you can ensure that the information is accurate and useful.

Practical Applications of QR Code Decoding
Decoding QR codes has numerous practical applications across various fields, enhancing efficiency and convenience. Understanding these applications can help you leverage QR codes effectively in your personal and professional endeavors.

Marketing and Advertising
Businesses use QR codes in marketing campaigns to provide quick access to promotional content, social media, or special offers. QR codes on advertisements enable consumers to engage with the brand instantly, enhancing the effectiveness of marketing efforts.
Applications of QR codes in marketing and advertising include:
-
Print Media: Embedding QR codes in magazines, newspapers, and flyers to direct readers to online content.
-
Outdoor Advertising: Placing QR codes on billboards, posters, and signage for instant access to promotions or information.
-
Product Packaging: Including QR codes on packaging to provide additional product details, user manuals, or special offers.
-
Event Promotions: Using QR codes on event posters and tickets to share event details and updates.
QR codes enhance the interactivity and reach of marketing campaigns, providing a seamless bridge between offline and online channels.

Inventory Management
In inventory management, QR codes streamline the tracking process, allowing for quick scanning and updating of product information. QR codes can store detailed product data, improving accuracy and efficiency in inventory management.
Applications of QR codes in inventory management include:
-
Product Identification: Assigning unique QR codes to products for easy identification and tracking.
-
Stock Management: Scanning QR codes to update stock levels, track movement, and manage inventory.
-
Order Fulfillment: Using QR codes to streamline the picking, packing, and shipping processes.
-
Asset Tracking: Monitoring the location and status of assets using QR codes.
QR codes enhance the accuracy and efficiency of inventory management, reducing errors and improving overall productivity.

Event Management
QR codes are widely used in event management for ticketing and attendee tracking. Scanning QR codes at entry points simplifies check-ins and enhances the overall event experience.
Applications of QR codes in event management include:
-
Ticketing: Issuing QR code tickets for quick and secure entry to events.
-
Attendee Management: Scanning QR codes to track attendee check-ins and manage attendance.
-
Event Information: Providing event schedules, maps, and updates via QR codes.
-
Networking: Facilitating networking by sharing contact information through QR codes.
QR codes improve the efficiency and convenience of event management, enhancing the experience for organizers and attendees alike.

Personal Use
For personal use, QR codes can store contact information, Wi-Fi passwords, or facilitate payments. They offer a convenient way to share information quickly and efficiently.
Applications of QR codes in personal use include:
-
Contact Sharing: Creating QR codes with contact details for easy sharing.
-
Wi-Fi Access: Generating QR codes with Wi-Fi network details for quick connection.
-
Payments: Using QR codes for secure and convenient payments.
-
Digital Content: Sharing links to websites, social media profiles, or digital content via QR codes.
QR codes provide a versatile and convenient tool for personal data sharing and management.
Tips for Creating Effective QR Codes
Creating effective QR codes involves ensuring they are easily scannable, choosing the right type of code, and customizing them for branding purposes. By following best practices, you can create QR codes that are functional and visually appealing.
Ensuring Scannability
To ensure scannability, design QR codes with sufficient contrast between the foreground and background, avoid overly complex designs, and test the QR code with various devices.
Best practices for ensuring scannability include:
-
High Contrast: Use high contrast colors for the QR code and background to ensure readability.
-
Adequate Size: Make the QR code large enough to be easily scanned, especially in print materials.
-
Clear Quiet Zone: Maintain a clear margin around the QR code to prevent interference from surrounding elements.
-
Simple Design: Avoid adding excessive design elements that can obscure the QR code.
Testing the QR code with multiple devices and scanning apps ensures that it can be reliably decoded in different environments.


Choosing the Right Type of QR Code
Select between static and dynamic QR codes based on the specific needs of your application. For information that might change, dynamic QR codes are more suitable.
Guidance on choosing the right type of QR code includes:
-
Static QR Codes: Use for fixed information that does not require updates, such as contact details or URLs.
-
Dynamic QR Codes: Opt for dynamic codes when you need the flexibility to update the encoded information or track usage.
Choosing the appropriate type of QR code ensures that it meets your specific requirements and provides the desired functionality.
Customizing QR Codes for Branding
Explore art QR codes with logos and colors to align with branding without compromising functionality. Tools like the ME-QR code generator make it easy to create customized QR codes that adhere to these best practices.
Create
QR Code Now!
Put your QR code link, add name for your QR, select content category and generate!
Tips for customizing QR codes for branding include:
-
Incorporate Logos: Add your logo to the QR code design without obscuring the data cells.
-
Use Brand Colors: Apply brand colors to the QR code while maintaining high contrast for readability.
-
Test Custom Designs: Ensure that customized QR codes are tested thoroughly to verify scannability.
By customizing QR codes, you can create visually appealing codes that reinforce brand identity while remaining functional.

Conclusion
QR codes are versatile tools with a wide range of applications, from marketing to personal use. Understanding how are QR codes decoded through learning their structure, and types is essential for leveraging their full potential. By using the right tools and techniques, you can even efficiently decode QR code without scanning.
As technology continues to evolve, QR codes are likely to play an even more significant role in our daily lives, making it crucial to stay informed about the latest developments and best practices.