Data Matrix vs. QR Code: Deciphering the Distinctions
To create a QR code for a link, video or picture - click on the button below.

The need for efficient and reliable data management solutions has become paramount. Among the many technologies developed to meet this need, Data Matrix and QR codes stand out for their versatility and widespread use.
This article delves into the difference between QR codes and data matrices, exploring their respective advantages, functionalities, and applications across various industries. By understanding these differences, businesses, and individuals can make informed decisions on which code type best suits their needs.
Introduction to Data Matrix and QR Codes
Data Matrix and QR codes are both types of two-dimensional (2D) barcodes that store data in a compact, machine-readable format. Unlike traditional linear barcodes, which store data in a series of lines and spaces, 2D barcodes use patterns of squares, dots, or other shapes to encode information. This allows them to store more data in a smaller space, making them ideal for a wide range of applications.

Overview of 2D Codes
2D codes, such as Data Matrix and QR codes, represent an evolution from the conventional linear barcodes. They are capable of storing significantly more information, which can include numeric, alphanumeric, binary, and even Kanji characters.
The key benefit of 2D codes is their ability to hold large amounts of data in a compact and easily scannable format. This capability has led to their widespread adoption across various sectors, with QR codes being particularly popular due to their ease of use and versatility.

Importance of Data Matrix and QR Codes
Both Data Matrix and QR codes have become integral tools in modern data management and logistics. They improve accuracy and efficiency in data entry, reduce errors, and facilitate quick access to information.
QR codes, in particular, have gained immense popularity due to their ease of scanning and widespread recognition, making them a preferred choice for many applications such as marketing, retail, and transportation.
Understanding QR Codes
To fully appreciate the capabilities and advantages of QR codes, it is essential to delve deeper into their structure, functionality, and common uses across various industries.

What is a QR Code?
A QR (Quick Response) code is a type of 2D barcode that can store various types of information, such as URLs, contact information, and text. It consists of black squares arranged on a white background, which can be scanned by a camera-equipped device to quickly retrieve the encoded information. QR codes are designed to be read quickly and easily, making them highly user-friendly.

How QR Codes Work
QR codes work by encoding data into a pattern of black and white squares. When scanned, the QR code reader decodes the pattern into a string of data. This process involves several steps, including image capture, binarization (converting the image to black and white), and decoding the pattern using Reed-Solomon error correction. This error correction capability ensures that QR codes can still be read accurately even if they are partially damaged or obscured.
Common Uses of QR Codes
QR codes are used in a wide variety of applications due to their versatility and ease of use. Some common uses include:





Healthcare: QR codes can store patient information, streamline check-ins, and manage medical records.
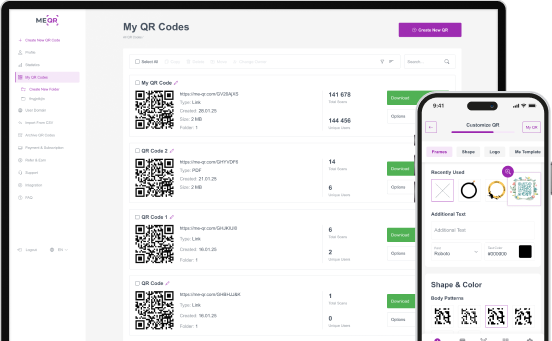
These examples illustrate the broad applicability and convenience of QR codes. For creating and managing these codes, ME-QR offers a user-friendly QR code generator, making it easy to implement QR codes in various applications.
Put your QR code link, add name for your QR, select content category and generate!
Put your QR code link, add name for your QR, select content category and generate!

Understanding Data Matrix Codes
Data Matrix codes also play a crucial role in various industries, particularly where space is limited, and high data capacity is required.

What is a Data Matrix Code?
A Data Matrix code is a type of 2D barcode that encodes data in a pattern of black and white cells. These codes can store large amounts of data in a small space, making them ideal for applications where space is limited. Data Matrix codes are particularly well-suited for encoding text and numeric data, and they are often used in manufacturing and logistics.

How Data Matrix Codes Work
Data Matrix codes work by encoding data into a pattern of square or rectangular cells. The pattern is read by a scanner, which converts the image into data using algorithms that decode the pattern. Like QR codes, Data Matrix codes use error correction techniques to ensure data can be accurately read even if the code is partially damaged.
Common Uses of Data Matrix Codes
Data Matrix codes are commonly used in industries where space is limited and high data capacity is needed. Common uses include:



These applications demonstrate the importance of Data Matrix codes in environments where efficient data encoding in limited space is crucial.
Data Matrix Code vs. QR Code: Key Differences
While both Data Matrix and QR codes are effective for different purposes, they have distinct differences that make them suitable for specific applications.

Visual Differences
Visually, Data Matrix and QR codes can be distinguished by their appearance. QR codes are generally larger and include distinctive patterns of squares and positioning markers in three corners.
In contrast, Data Matrix codes are more compact and can appear as square or rectangular patterns of dots or squares, without the positioning markers seen in QR codes.

Encoding Capabilities
Both types of codes encode information using different techniques. QR codes can store numeric, alphanumeric, binary, and Kanji data types, making them highly versatile.
Data Matrix codes, while also capable of encoding a variety of data types, are often used for smaller amounts of data due to their compact size and efficiency.

Size and Capacity
When it comes to size and data capacity, QR codes typically provide a good balance, being easily readable while storing significant amounts of data.
Data Matrix codes can store a large amount of data relative to their size, making them useful for applications where space is at a premium.

Error Correction Levels
Error correction is crucial for ensuring data integrity in barcodes. QR codes use Reed-Solomon error correction, which allows for up to 30% of the code to be damaged without data loss.
Data Matrix codes also have robust error correction capabilities, but QR codes are generally more reliable in terms of error correction performance.

Readability and Scanning Speed
QR codes are designed for quick and easy scanning, making them highly user-friendly and efficient. Their design and widespread use mean that many devices and applications are optimized for reading QR codes, ensuring fast and reliable scanning.
Data Matrix codes, while also reliable, may not be as intuitively scanned by all devices, particularly consumer-grade equipment.
QR vs. Data Matrix in Different Industries
Both Data Matrix and QR codes find applications across various industries, but their effectiveness can vary depending on the specific requirements of each industry.

Data Matrix vs. QR Code in Manufacturing
In manufacturing, both Data Matrix and QR codes are used for tracking and quality control. Data Matrix codes are favored for their compact size and high data capacity, making them ideal for marking small components. However, QR codes are often preferred for their ease of use and widespread recognition.

QR Code vs. 2D Matrix in Retail
In the retail sector, QR codes are widely used for product information, marketing, and customer engagement. Their ability to store URLs and other data types makes them perfect for connecting customers to digital content. Data Matrix codes are less common in retail due to their less intuitive design and scanning requirements.

GS1 Data Matrix vs. QR Code in Logistics
In logistics, both GS1 Data Matrix and QR codes are used to manage supply chains and track shipments. While Data Matrix codes are effective for encoding large amounts of data in a small space, QR codes are typically preferred for their versatility and ease of scanning.
Data Matrix vs. QR: Advantages and Disadvantages
Both QR codes and Data Matrix codes come with their own sets of advantages and disadvantages, which can influence their suitability for different applications.

Pros and Cons of Using QR Codes
Using QR codes offers several advantages and some potential drawbacks.
-
Easy to scan and use with consumer devices.
-
Versatile data encoding capabilities.
-
Robust error correction.
-
Widely recognized and used.
-
Larger physical size compared to Data Matrix codes.
-
Can be less space-efficient.
These pros and cons highlight why QR codes are popular in many consumer-facing applications, despite their larger size.
Pros and Cons of Using Data Matrix Codes
Data Matrix codes also offer unique benefits and some limitations.
-
High data capacity in a compact size.
-
Effective for small components and products.
-
Robust error correction.
-
Less intuitive design and scanning process.
-
Not as widely recognized as QR codes.
These characteristics make Data Matrix codes particularly suitable for industries where space and data capacity are critical considerations.
Choosing Between Data Matrix and QR Codes
Deciding a data matrix barcode vs. QR code depends on several factors, including the specific requirements of your industry and application.

Factors to Consider
When deciding between Data Matrix and QR codes, consider the following factors:
-
Data Needs: QR codes are better for encoding URLs and various data types, while Data Matrix codes excel in space-efficient data storage.
-
Space Constraints: Data Matrix codes are ideal for small spaces, whereas QR codes require more space but offer greater versatility.
-
Scanning Technology: QR codes are more user-friendly and widely supported by consumer devices through a QR Code Scanner.
This data matrix vs. QR code comparison can help guide your decision on which type of code is more suitable for your needs.
Industry-Specific Recommendations
For most applications, QR codes are recommended due to their versatility and ease of use. However, in industries where space is limited and high data capacity is essential, such as manufacturing and healthcare, Data Matrix codes may be more suitable.

Conclusion
Both Data Matrix and QR codes offer unique advantages and are suited to different applications. While Data Matrix codes are highly efficient in terms of space and data capacity, QR codes are generally more versatile, easier to use, and widely recognized. When choosing between the two, consider the specific needs of your industry and application. Overall, QR codes often provide a better balance of functionality and user-friendliness, making them a popular choice in many fields.